

Things to Remember Based on Mitosis Stages The nucleus then enters the interphase phase. When seen under a light microscope, it resembles with a single thread. The nucleoli can also be found near the poles.Ĭhromosomes begin to uncoil and unfold and form a thin and long chromosome. This new membrane forms on each of the poles and covers the chromosomes. The spindle tubes begin to dissolve and a membrane is formed. The final stage i.e telophase starts when the chromosomes reach the pole. Each of the chromatids becomes a chromosome after the separation. The chromatids then begin to separate and move to one of the poles on each side. Also, each chromatid is connected to a spindle tube.
#Prophase 2 definition free
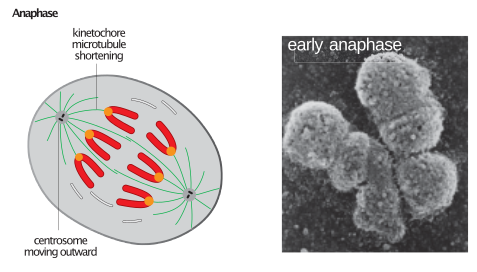
Each chromatid of the chromosome are free at the centromere. The chromatids split at the centromere during anaphase. AnaphaseĪnaphase is the third stage of mitosis. The sister chromatids of each chromosome are linked at the centromere, but their arms remain free. The chromosomes can be seen clearly during metaphase. A spindle tube connects the chromosome to the centromere. The spindle tubes are produced at this stage, and the chromosome is orientated in the centre at the equatorial plate. The nucleolus and nuclear membrane vanish after the prophase stage. Under a microscope, the two chromatids of each chromosome housed in the centromere are visible in the centre. It looks thick, short, and more prominent in the late prophase. The chromosome becomes coiled and short, as well as more distinguishable, during mid-prophase. The chromosome looks like a thin, uncoiled thread during the early prophase. ProphaseĪfter the G2 stage of interphase, the prophase begins. The resting period is called G1, S is the stage at which DNA replication takes place, and G2 is again the stage of resting after the DNA replication.


It is divided into the G1, S and the G2 sub-phases. Interphase leads to the process of mitosis. The interphase is not a phase of mitosis, but it is still a very important process. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase are the stages of mitosis. Mitosis is divided into phases, each corresponding to the end of one set of activities and the beginning of the next. The mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle is the phase in which the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells occurs at each phase of Mitosis. The cells are broken up into a sequence of well-organized stages. During the mitotic stage, the cells do not divide their DNA at random. They might die or develop cancer if they don't survive. This does not function correctly if the cells have too many or very few chromosomes. The primary goal of Mitosis is to ensure that every daughter cell produced has a complete and flawless set of chromosomes. The mitotic division is a method of reproduction for single-celled eukaryotes, in which new individuals are added to the population. Throughout the lifetime, mitosis replaces old cells with new ones. The process of mitosis fills the body of an organism with cells during its growth and development. Mitosis is responsible for the majority of cell divisions in our body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
